Database
Database types
- RDBMS (= SQL/ OLTP): RDS.Aurora - great for joins
- NoSQL database:
- DynamoDB (~]SON)
- ElastiCache (key / value pairs).
- Neptune (graphs) - no joins, no SQL
- Object Store: S3 (for big objects) / Glacier (for backups / archives)
- Data Warehouse (= SOL Analytics / BI): Redshift (OLAP - Online analytics processing), Athena
- Search: ElasticSearch (SON) - free text, unstructured searches
- Graphs: Neptune - displays relationships between data
DBs
RDS
- Operations: small downtime when failover happens, when maintenance happens, scaling in read replicas / ec2 instance / restore EBS implies manual intervention, application changes
- Security: AWS responsible for OS security, we are responsible for setting up KMS, security groups, lAM policies, authorizing users in DB. using SSL
- Reliability: Multi AZ feature, failover in case of failures
- Performance: depends on EC2 instance type, EBS volume type, ability to add Read Replicas. Doesn't auto-scale
- Cost: Pay per hour based on provisioned EC2 and EBS
Aurora
- Operations: less operations, auto scaling storage
- Security: AVVS responsible for OS security, we are responsible for setting up KMS, security groups, lAM policies, authorizing users in DB, using SSL.
- Reliability: Multi AZ, highly available, possibly more than RDS,Aurora Serverless option.
- Performance: 5x performance (according to AVVS) due to architectural optimizations. Up to 15 Read Replicas (only 5 for RDS)
- Cost: Pay per hour based on EC2 and storage usage. Possibly lower costs compared to Enterprise grade databases such as Oracle
ElastiCache
- Operations: same as RDS
- Security. AWS responsible for OS security, we are responsible for setting up KMS, security groups, AM policies, users (Redis Auth), using SSL
- Reliability: Clustering, Multi AZ
- Performance: Sub-millisecond performance, in memory, read replicas for sharding, very popular cache option
- Cost: Pay per hour based on EC2 and storage usage
DynamoDB
- Operations: no operations needed, auto scaling capability serverless
- Security: full security through AM policies, KMS encryption, SSL in flight
- Reliability: Multi AZ, Backups
- Performance: single digit millisecond performance, AX for caching reads, performance doesn't degrade if your application scales
- Cost: Pay per provisioned capacity and storage usage (no need to guess in advance any capacity - can use auto scaling)
Aurora
- Operations: no operations needed
- Security: AM. Bucket Policies, ACL. Encryption (Server/Client), SSL
- Reliability: 99.999999999% durability / 99.99% availability, Multi AZ, CRR
- Performance: scales to thousands of read / writes per second, transfer acceleration / multi-part for big files
- Cost: pay per storage usage. network cost, requests number
Redshift
- Operations: similar to RDS
- Security: IAM.VPC, KMS, SSL (similar to RDS)
- Reliability: highly available, auto healing features
- Performance: 10x performance vs other data warehousing, compression
- Cost: pay per node provisioned, I/IQ' of the cost vs other warehouses
- Remember: Redshift = Analytics / BI / Data Warehouse
ElasticSearch
- Operations: similar to RDS
- Security: Cognito, IAM,VPC, KMS. SSL
- Reliability: Multi-AZ. clustering
- Performance: based on ElasticSearch project (open source), petabyte scale
- Cost: pay per node provisioned (similar to RDS)
- Remember: ElasticSearch = Search / Indexing
Tools
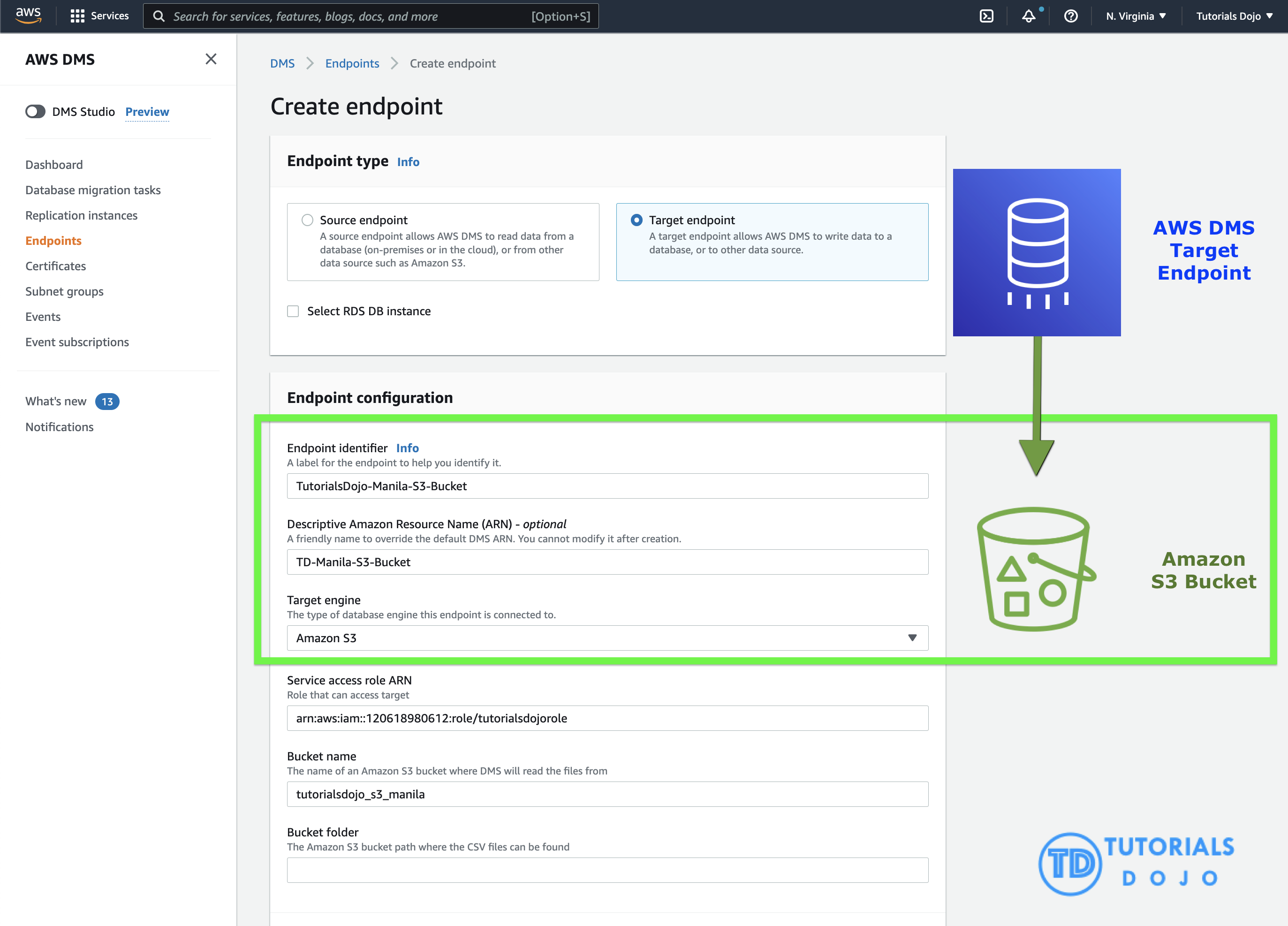
AWS DMS
AWS Database Migration Service (AWS DMS) is a cloud service that makes it possible to migrate relational databases, data warehouses, NoSQL databases, and other types of data stores. You can use AWS DMS to migrate your data into the AWS Cloud or between combinations of cloud and on-premises setups.
DMS + AWS Macie
One combination that you could use is to set S3 as a Target of AWS DMS, then once the data is fully copied to S3, create a Macie classification job to analyze the S3 objects. Reference: Using Amazon S3 as a source for AWS DMS
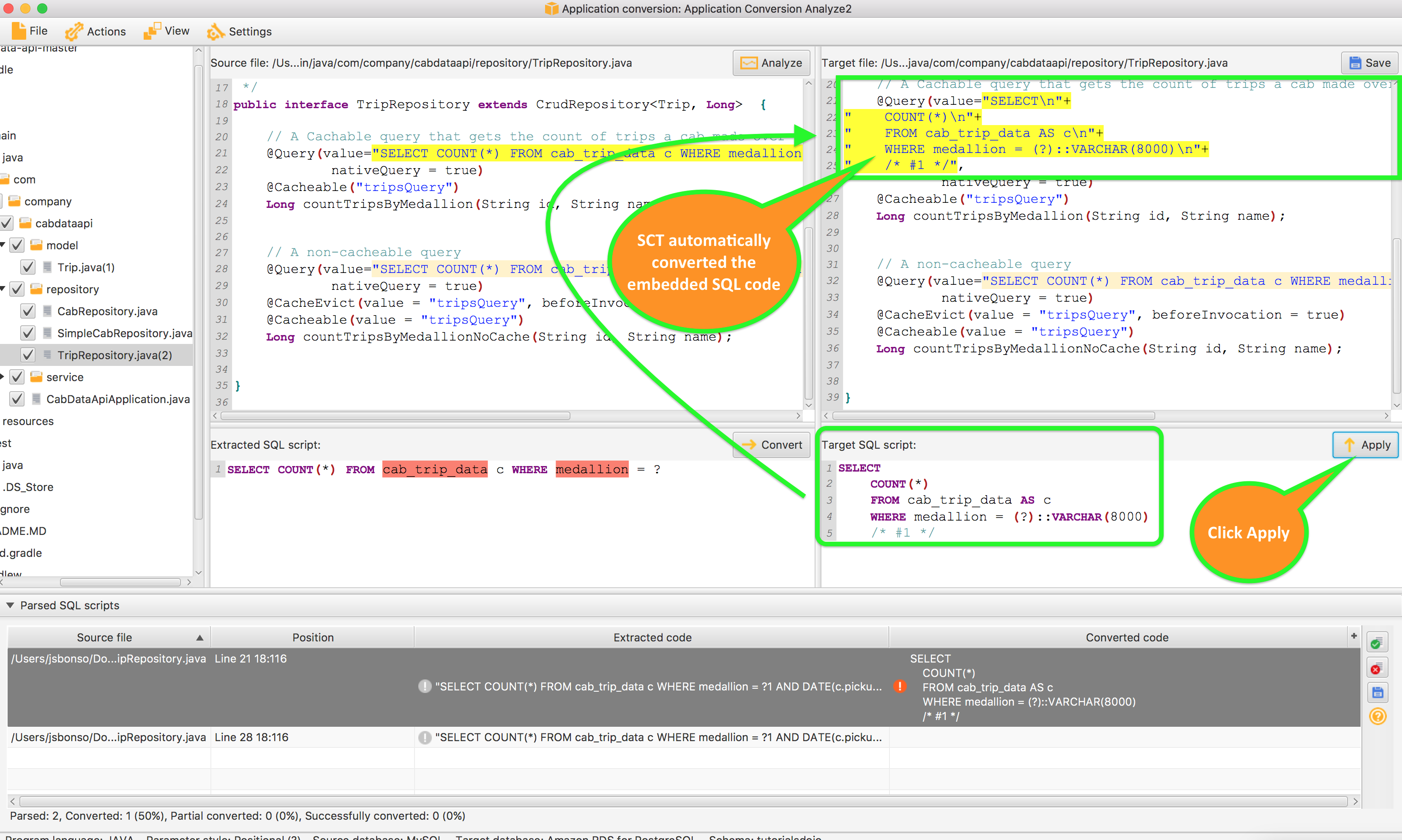
AWS Schema Conversion Tool(SCT)
AWS offers two schema conversion solutions to make heterogeneous database migrations predictable, fast, secure, and simple. Customers have the choice to:
- Log in to the AWS Database Migration Service (AWS DMS) console to initiate the AWS DMS Schema Conversion (DMS SC) workflow for a fully managed experience
- Download the AWS Schema Conversion Tool (AWS SCT) software to their local drive.
The target engines can be Oracle, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, and MySQL.